Against a background of ever-keener commercial competition, the shopping experience has become one of the new differentiating features. The shopping experience, briefly put, is “the totality of the emotions, feelings and stimuli felt by a user throughout the process.” Although this can apply to any sector, this article will focus on retail. So for our purposes the definition becomes the “totality of the emotions, feelings and stimuli felt by a consumer (i.e. a customer or a prospect) throughout the shopping experience”
Importance of the shopping experience
Why is “improving the shopping experience” an increasingly important topic for enterprises? One of the main answers to this question can be summed up as follows:
A “happy” user = a “loyal” user (and an “ambassador")
From a statistical point of view, numerous studies have shown that its costs around five times as much to acquire new customers as to retain them. As retention is dependent, inter alia, on an optimal experience, it is important to make it as efficient as possible.
The best advertising is a satisfied customer.
Bill Gates
Measurement and Net Promoter Score
The Net Promoter Score, or NPS, is one of the main performance indicators for the shopping experience.
What is it?
The NPS consists of a question posed at the end of the experience, in the following form:
On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend […the value proposition of the enterprise…] to a friend?
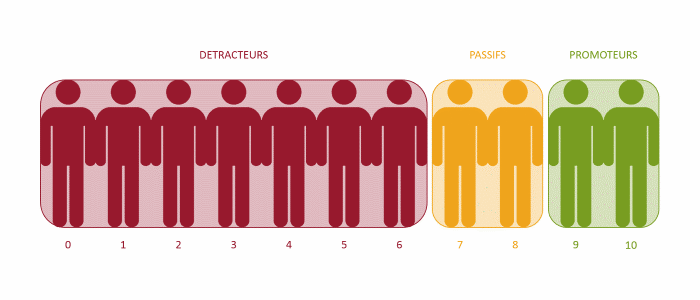
There are three types of respondents:
- Promotors give a score of between 9 and 10. These are the individuals most likely to recommend your value proposition, so they must be encouraged, perhaps by suggesting that they should write up their opinion and share it on social media,
- Between 7 and 8, respondents are described as ‘passive’,
- while between 0 and 6, they are ‘detractors’.
How is the NPS measured?
The NPS is measured as follows:
% of promoters – % of detractors = NPS
Example: 100 respondents, 35 promoters, 40 passive, 25 detractors >>> the NPS is +10 (35-25).
At what points can the question be asked?
There are a number of methods of collecting the NPS.
Two main questions should be considered:
- Do you want to analyse all or part of the buying journey? In the first case, the NPS will be posed at the end of the journey; in the second case, it may be posed either during (which may damage the experience) or at the end of the journey.
- By what method?
Here is a non-exhaustive list of possible contact methods that can be used:
- SMS
- Push notification
- Telephone (ideally via a questionnaire without “face-to-face”)
- Sales point terminal
- The web site (e.g. a banner after confirming the order)
- The QR code
- Social networks
- Etc.
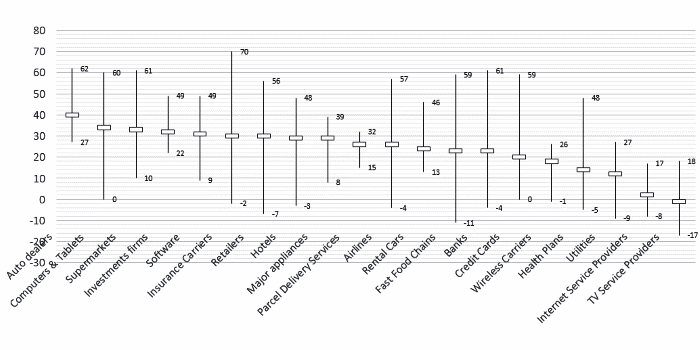
Market averages
Here is a selection of averages by business sector (United States, 2015).
Methodology for identifying ways to improve the shopping experience (retail sector)
In order to improve the shopping experience for your customers, you should follow these “ten commandments”.
1. Be empathetic
The first step consists of adopting an empathetic approach, putting yourself in the place of your customer, in order to accept, listen to and understand the problems they encounter. This attitude is very important and must be maintained throughout all the stages suggested here. You can routinely ask yourself the question: What if I were the customer (or prospect)?
2. Offer infinite journeys
Today, many of you know that purchasing journeys vary greatly from one customer to another. Retail has undergone many changes. Once a single-channel operation, it then became cross-channel, then omni-channel and is now unified. We won’t run through these transformations again in this article; it is enough to note that the journey now consists of an ever-increasing number of contact points.
To aid comprehension of the following stages, we will identify four purchasing journeys which themselves include a multitude of other journeys, namely:
- Research Online Purchase Offline (ROPO)
- Showroom
- Full web
- Full store
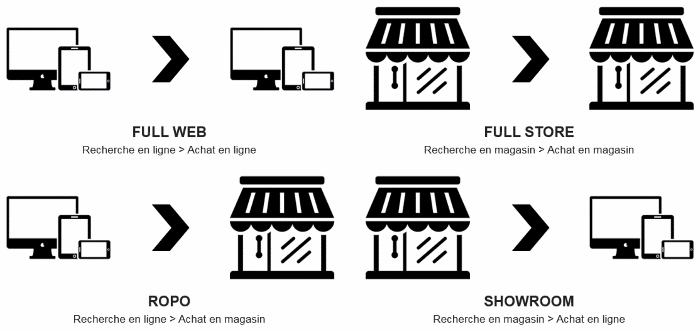
Research online > Purchase online Research offline > Purchase offline
Research on line > Purchase offline Research offline > Purchase online
3. …and break them down
There are several ways of breaking down these journeys, all deriving from different methodologies.
- First method: Attention > Research > Decision > Purchase
- Second method: Awareness > Consideration > Purchase > Retention > Advocacy
- Third method: Acquisition > Activation > Retention > Referral
- etc.
We suggest that you use this third approach. Thus, we will define each of the steps as follows:
- ACQUISITION: What must be done to publicise the company’s value proposition?
- ACTIVATION: How can prospects be converted into customers?
- RETENTION: How are customers retained?
- REFERRAL: How are customers transformed into ambassadors, so as to create recommendations?
Applied to the four main journeys listed above, we can define a number of KPIs.
| ROPO | Full store | Showroom | Full web |
| Acquisition | Number of prospects coming through the door | Number of prospects visiting my digital platforms (e.g. website, mobile app, etc.) | |
| Activation | Number of prospects converted into customers | ||
| Retention | Number of customers returning to the shop | Number of customers returning to my digital platforms (e.g. website, mobile app, etc.) | |
| Referral | Number of prospects coming through the door thanks to word of mouth | Number of prospects visiting my digital platforms (e.g. website, mobile app, etc.) thanks to word of mouth |
4. Gather and analyse verbatims
As previous mentioned, there are many ways of measuring the NPS. What we have not clarified is that it is possible, under certain conditions, to ask an open question. For example, people who give a score of 6 or less could be asked: In order to improve our services, could you please tell us about the problems you’ve encountered?
These responses (phrases) are called verbatims and identify the inconveniences encountered by your users.
These should then be analysed, categorised and finally weighed up.
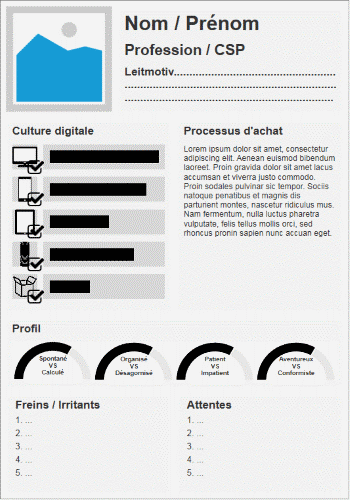
5. Identify and satisfy personas
A persona is a typical user, an archetype, pictured in identity card format, including:
- a photo
- a family name and first name
- gender
- profession and associated socio-professional category
- age group
- family composition
- the typical day
- areas of interests,
- relationship with technology (devices owned and level of use)
- goals
- expectations
- potential obstacles
- etc.
Ideally, they are assembled on the basis of the verbatims, so as to cover the entire population surveyed.
6. Suggest or receive ideas
Brainstorming sessions can be organised. They can be attended just by staff. Or they can also admit the end users who, incidentally, will feel very valued to be involved in jointly developing the company strategy. Many methods exist, meeting different objectives:
- Gathering the suggestions of all the participants
- Ideas challenge
- etc.
Note that new and rather original methods are being developed, such as Lego Serious Play. This method asks all participants to build digital platforms in Lego.
Innovative technologies (virtual reality, augmented reality, beacons, artificial intelligence, chatbots, voicebots, etc.) can very easily be used in discussions.
7. Design prototypes
It is important to design the interfaces of your future digital platforms, first with a show of hands and later using prototyping software. This enables all participants to understand the results of the previous brainstorming sessions.
8. … and have them tested by real users
This stage is essential. It enables you to validate or reject the choices made in earlier stages.
9. Accept setbacks
Setbacks are entirely possible at the previous stage. In this instance, an agile attitude will enable you to bounce back and start a new iteration of steps 7 and 8.
10. Lastly, introduce your improvements
Finally, during this last stage, teams of developers will be asked to develop the functionalities and journeys identified in the previous stages.
Business & Decision, with its 20 years of experience, can support your teams and lead these various working sessions. The group has also had the opportunity to work in numerous digital areas, enabling it to rapidly identify new ways of improving the shopping experience. Don’t hesitate to contact us.













Your email address is only used by Business & Decision, the controller, to process your request and to send any Business & Decision communication related to your request only. Learn more about managing your data and your rights.